Articles / PFAS / Sustainability / Water pollution
PFAS: Uses, Exposure, and Environmental Impact
Understanding PFAS: Uses, Exposure, and Environmental Impact
March 3, 2025
Understanding PFAS: Uses, Exposure, and Environmental Impact
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of synthetic chemicals that contain a chain of carbon and fluorine atoms. Since the carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry, the bond strength is the primary reason PFAS are described as ‘forever chemicals’ and known to be persistent in the environment, as they do not degrade in conventional treatment processes for both wastewater and drinking water.

Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have become a topic of significant concern due to their widespread use and persistence in the environment.
Understanding PFAS
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have become a topic of significant concern due to their widespread use and persistence in the environment. Known for their hydrophobic and oleophobic properties, these chemicals have found their way into a multitude of consumer products. From nonstick cookware to stain-repellent clothing, PFAS are integral to the production of items designed to resist water, grease, and stains. However, the environmental and health implications of these “forever chemicals” are prompting closer scrutiny.
Which Products Contain PFAS
PFAS are prevalent in various consumer product categories, including:
- Clothing: Items labelled as stain-repellent or water-resistant, such as raincoats and workwear, are often treated with PFAS.
- Children’s Products: Bedding, soft toys and children’s clothing/footwear.
- Personal Care Products: Items include shampoo, dental floss, nail polish and cosmetics.
- Furniture and Decor: Carpets, rugs, and other textiles often incorporate PFAS for stain repellent.
- Household Products: Nonstick cookware, cleaning solutions, paints, adhesives and sealants.
Additionally, PFAS may be present unintentionally as byproducts or contaminants from the manufacturing process.
The persistence and mobility of PFAS make them particularly troublesome, as they can move between different environmental media, exacerbating their spread and impact.
PFAS Environmental Impact
The discharge of environmental contaminants into surface water, release into the air, and leaching the soil and groundwater has become a predominant concern due to industrialisation.
With such a wide range of uses, PFAS can readily enter the environment during manufacture or formulation, use of the substances themselves or products containing them, and through end-of-life disposal. Their stability and resistance to degradation results in almost indefinite environmental contamination, leading to long-term continuous exposure of people and wildlife.
PFAS have been detected in the bloodstreams of wildlife and humans globally. In wildlife, exposure occurs mainly through contaminated water, air, and food sources. Humans face similar exposure routes, with additional risks from cosmetics, clothing, and household dust.
PFAS Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation refers to the gradual accumulation of substances, such as PFAS, in an organism. This process occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than it can be excreted. Over time, the concentration of PFAS in the organism increases. This can happen through various pathways, such as:
- Working in occupations such as firefighting, chemical manufacturing or processing.
- Consuming contaminated water or food.
- Breathing in air or dust particles that contain PFAS.
- Skin contact with PFAS-contaminated surfaces or products.
The bioaccumulation of PFAS chemicals presents a complex challenge that affects ecosystems and human health alike. While progress is being made in understanding and mitigating these risks, continued research and regulatory efforts are essential. By working together, scientists, policymakers, and the public can help reduce the prevalence of PFAS and safeguard our planet for future generations.
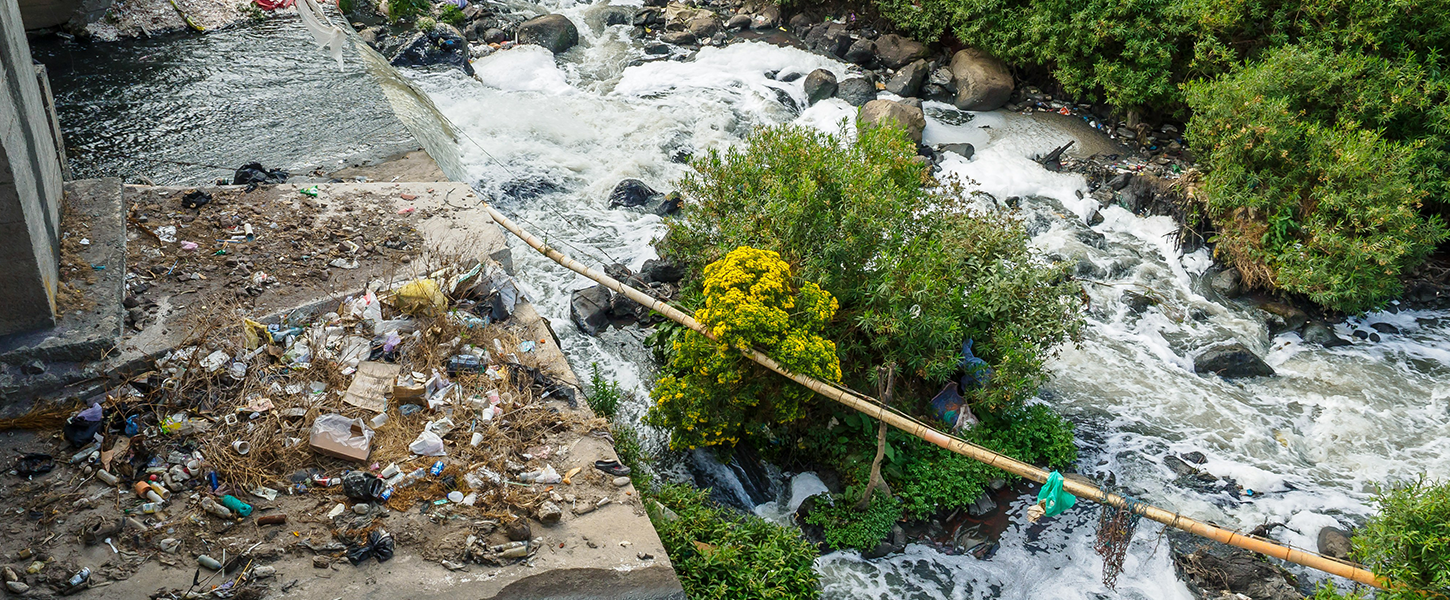
There have been growing concerns regarding the pollution and health implications of legacy PFAS.
PFAS Remediation
There have been growing concerns regarding the pollution and health implications of legacy PFAS, especially PFOA and PFOS, and this has led to regulatory controls being put into place. The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organics Pollutants is an international treaty aiming to eliminate or restrict the production and use of the most toxic chemicals of global concern. Currently, three sub-group of PFAS are listed in the convention: PFOS and related substances since 2009 for global restriction; PFOA and related substances since 2019 for global elimination and PFHxS and related substances since 2022 for global elimination without exemptions.
Addressing PFAS legacy contamination presents formidable challenges. The high cost of remediation, coupled with the difficulty of assigning responsibility for cleanup, often leads to legal disputes. Regulatory efforts to manage PFAS waste and contamination are complicated by the need for robust monitoring and enforcement. As regulations evolve, industries must navigate the complexities of liability and remediation strategies.
While PFAS offer valuable properties for consumer products, their persistence and potential health impacts necessitate careful consideration and management. Ongoing research and regulatory measures will be crucial in mitigating the risks associated with these pervasive chemicals. While progress is being made in understanding and mitigating these risks, continued research and regulatory efforts are essential. By working together, scientists, policymakers, and the public can help reduce the prevalence of PFAS and safeguard our planet for future generations.
About Arvia
Arvia is one of the world’s leading manufacturers of electrochemical water treatment products.
With design, manufacturing, and R&D in the UK, they also have labs in India, a facility in China and have expanded into the US.
Arvia’s treatment systems include Nyex Florenox™, Nyex Rosalox™ and Ellenox™ – three revolutionary systems specifically designed for tertiary water treatment, each delivering spectacular (up to parts per billion) results treating many recalcitrant pollutants in industrial wastewater like PFAS, endocrine disruptors and antibiotics.
To see how Arvia Technology could benefit many water treatment systems worldwide, check the Arvia website or make contact to set up a one-to-one consultation with a water science expert.
More featured articles
03.13.2025
In this article, we discuss World Kidney Day, and the heightened risks of Chronic Kidney Disease from increased exposure to PFAS.
02.3.2025

This article examines the health risks of PFAS-contaminated water, including a higher risk of cancer and other harmful effects.
01.13.2025

The theme of this year's World Economic Forum is “Collaboration for the Intelligent Age." This will highlight the potential for intelligent systems to address the planetary crisis and forge a nature-positive, net zero and resilient future.
Our wastewater treatment expertise
Our water technology can be used to treat a variety of water treatment applications. Once we understand the nature of your wastewater and your final water quality target, our water treatment specialists can make recommendations as to how best to treat your water. Take a look at some of the Nyex applications here:
Need help? Speak with an expert
