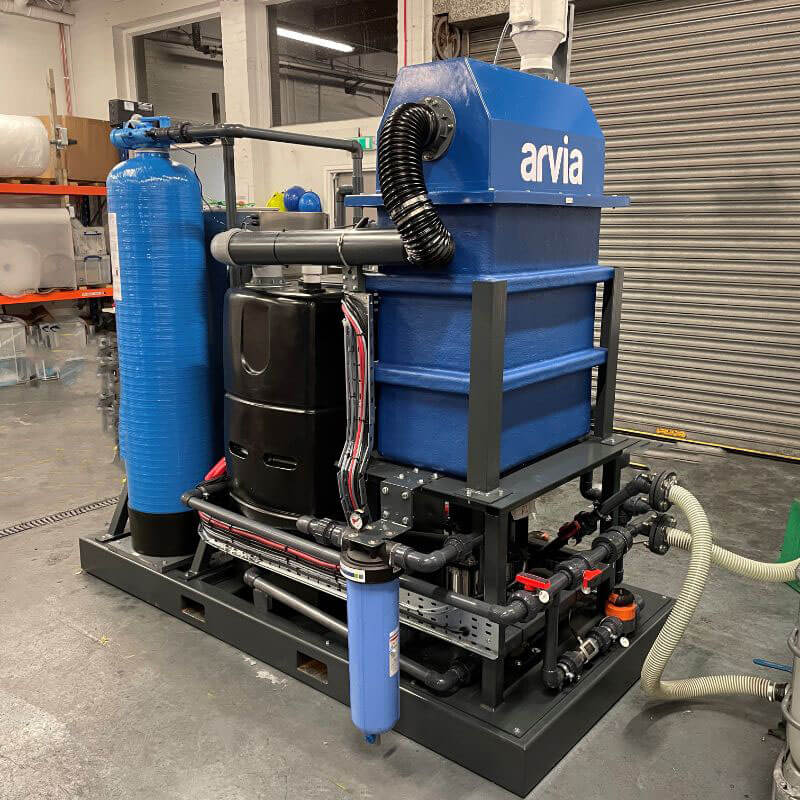
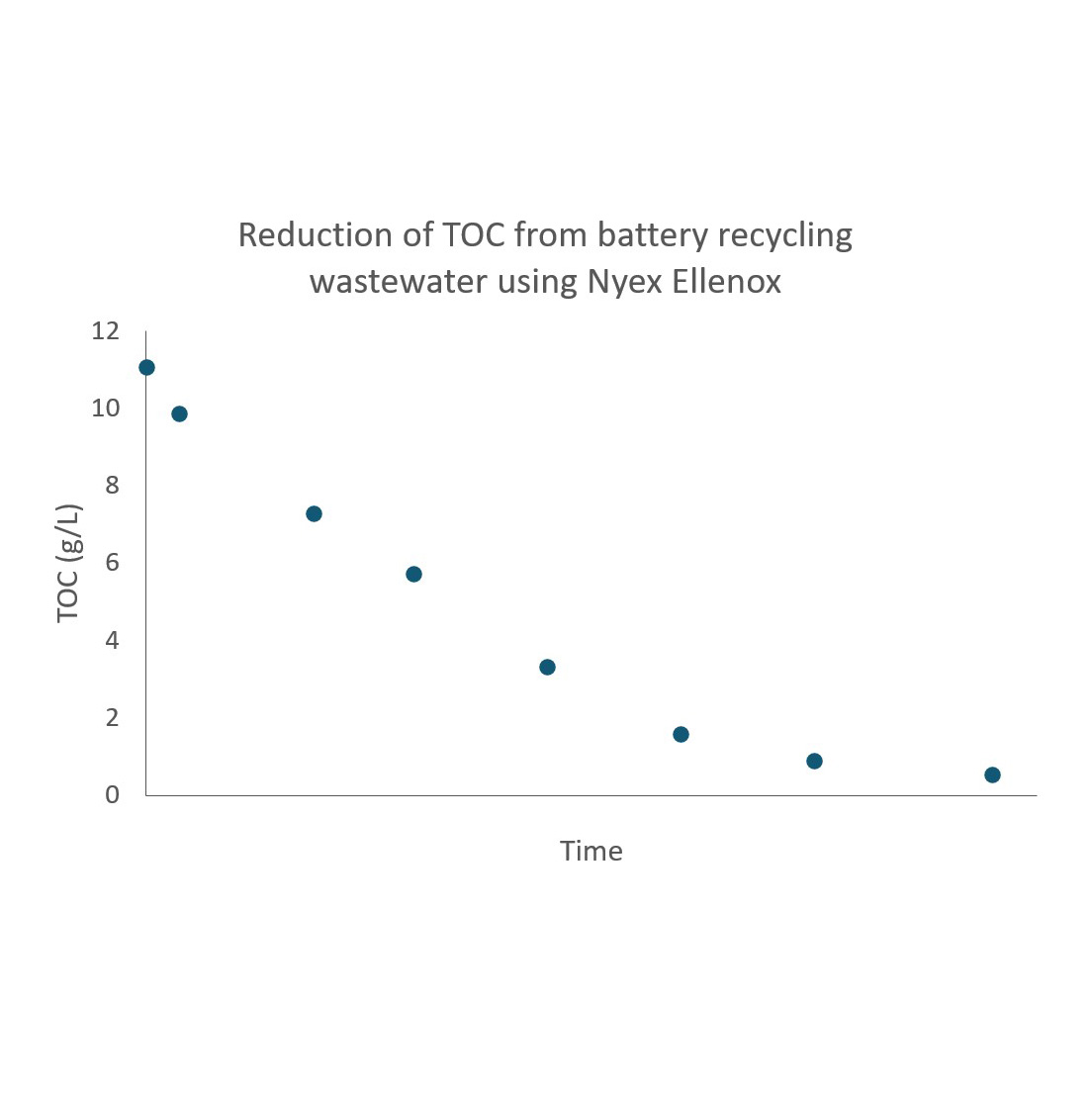
Case Study: EV Battery Recycling Water Treatment
Within the lithium battery manufacturing industry, there has been a major push towards the recycling and reuse of lithium batteries. This is due to the growing demand for lithium batteries in numerous applications including Electrical vehicles, consumer electronics and industrial appliances.